Partial Double Bond Character of Peptide Bond
The evidence that shows this partial double bond character is from the length of the bond. The planarity and rigidity of the peptide bond are accounted for by the fact that free rotation cannot occur around double bonds.

Structural Biochemistry Organic Chemistry Important Organic Reactions In Biochemistry Peptide Bonding Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
Thus the partial double bond character of CN in the peptide group means that this bond is shorter than would be predicted for a CN single bond whilst the CO bond having a partial single bond character due to resonance is longer than would be predicted for a CO double bond.
. A partial pi bond can also cause a partial triple bond. The partial double-bond character of the bond that links the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen of a peptide renders four atoms of the peptide bond coplanar and restricts the number of possible peptide conformations. Resonance of peptide bond.
The partial double bond character of peptide bond prevent free rotation of polypeptide chain. The peptide bond is planar because resonance is possible when all nonbonding electrons and empty orbitals are in the same plane ie. Greatly reduced rotational freedom compared to the φ phiψ psi torsion angles.
The carbonyl oxygen has a partial negative -028 charge and is a good hydrogen bond acceptor while the amide nitrogen is partially positive 028 and a good hydrogen bond donor. The partial double bond nature of the peptide bond is known to have an impact on the protein structure. The short carbonyl carbonnitrogen bond length 0132 nm the usual carbonnitrogen single bond length is 0147 nm is consistent with the partial double-bond character of the peptide linkage.
Rotation around the peptide bond is known to be restricted. A partial double bond is indicated with two parallel lines like a normal double bond. Second because of resonance the peptide bond has partial double-bond character which.
The amide structure has two resonance contributors. This is because only the alpha carbons in a protein backbone. Peptide bond has partial double bond character so it is shorter than single bond and longer than double bond.
While drawn as a single bond the peptide bond has partial double bond character that enforces a well-defined flat structure. The polarity of the peptide bond can make an important contribution to the behavior of folded proteins as discussed later in section 1-6. The peptide bond is trans It never occurs in cis configuration due to steric hindrance.
What is a major consequence of the partial double bond character. The peptide bond has a partial double-bond character- that is. Thus the peptide bond has a partial double bond character and exhibits limited rotation eliminating choice C.
A partial triple bond has a bond order between 2 and 3. -The peptide bond exhibits partial double bond character -The peptide bond has restricted rotation around the bond between the carbonyl carbon and C. The rigid planar nature of the peptide unit has.
The peptide bond has a partial double bond character because the double bond can resonate between CO and CN. Chemistry questions and answers. As resonance leads towards stability it prefers to stay in trans planner configuration.
One solid line and one dashed line. Generally speaking peptide bonds are in the trans conformation. The peptide bond is a stable covalent bond and is said to be a rigid planar bond because it has a partial double bond character.
Partial double bonds are caused by resonance in a structure which is the transfer of π electrons those which form the second bond in a double bond from one site to another. The peptide bond is rigid and planar with a partial double bond in character. They are listed above.
Peptide bonds have partial double bond character owing to possible resonance structures and delocalization of electrons. For the following charged amino acids at pH 7 determine whether the net charge on the amino acid is positive negative or neutral. The O atom of the amide has a partial negative charge and is a good hydrogen bond acceptor while the NH is partially positive and a good hydrogen bond donor.
Both CO and NH groups of peptide bonds are planar and are involved in hydrogen bond formation. This prevents free rotation around the bond between the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen of the peptide bond. Thus peptide bond attains a planar geometry and sp 2 hybridisation.
Peptide bond is rigid and planner. While drawn as a single bond the peptide bond has partial double bond character that enforces a well-defined flat structure. There is a partial double bond character in a peptide bond.
Because the bond between the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen has a partial double bond character rotation around this bond is restricted. Lack of rotation around the bond. -The peptide bond is planar.
In the diagram of a peptide shown which bonds are not free to rotate due to the partial double bond character. Thus the peptide unit is a planar rigid structure and rotation in the peptide backbone is restricted to the bonds involving the a carbon. It is shorter than a single bond and is therefore rigid and planar.
Peptide bond possesses a partial double bond character of C-N bond due to delocalisation of unshared pair of electrons coming from nitrogen into the carbonyl group CO. It is 013 Angstrom shorter than the C-N single bond yet not as short as a double bond. A partial double bond has a bond order between one and 2.
There are about three major characteristics of a peptide bond. Like a double bond sp 2 hybridization. The dipole momentof each peptide bond is shown in Figure 1-8.
It generally exists in trans-configuration. Resonance Structure of Peptide Bond.
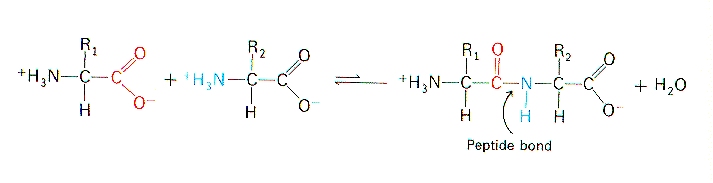
Peptide Bond The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki
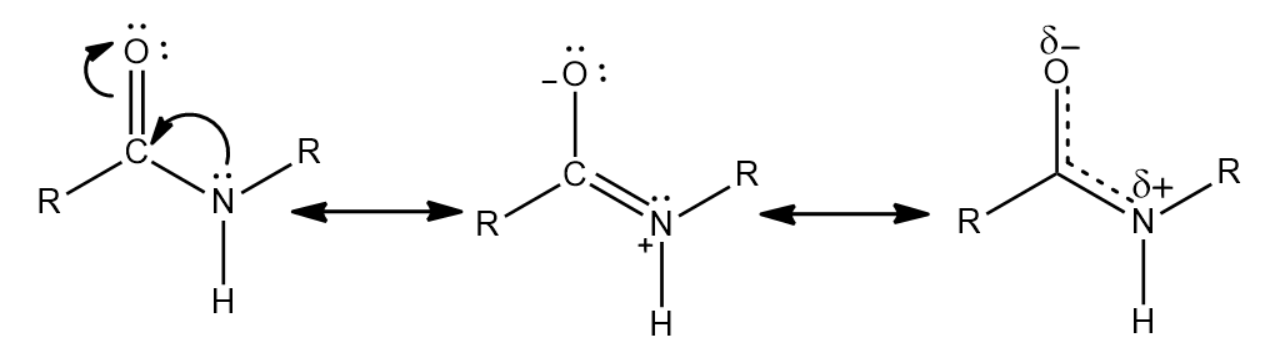
What Is A Major Consequence Of The Partial Double Bond Class 11 Chemistry Cbse
No comments for "Partial Double Bond Character of Peptide Bond"
Post a Comment